Choosing the right degree of centralization is not a theoretical exercise. It is a strategic decision influenced by internal capabilities, external pressures, and leadership philosophy.
Organizations that centralize without understanding these factors often struggle with rigidity, delays, or disengagement. Those that evaluate them carefully are more likely to design structures that balance control, efficiency, and adaptability.
This article explains the key factors affecting centralization, helping managers decide when centralization works, when it fails, and how much is appropriate. For a complete overview of the concept, see our detailed guide on centralization in management.
What Are Factors Affecting Centralization?
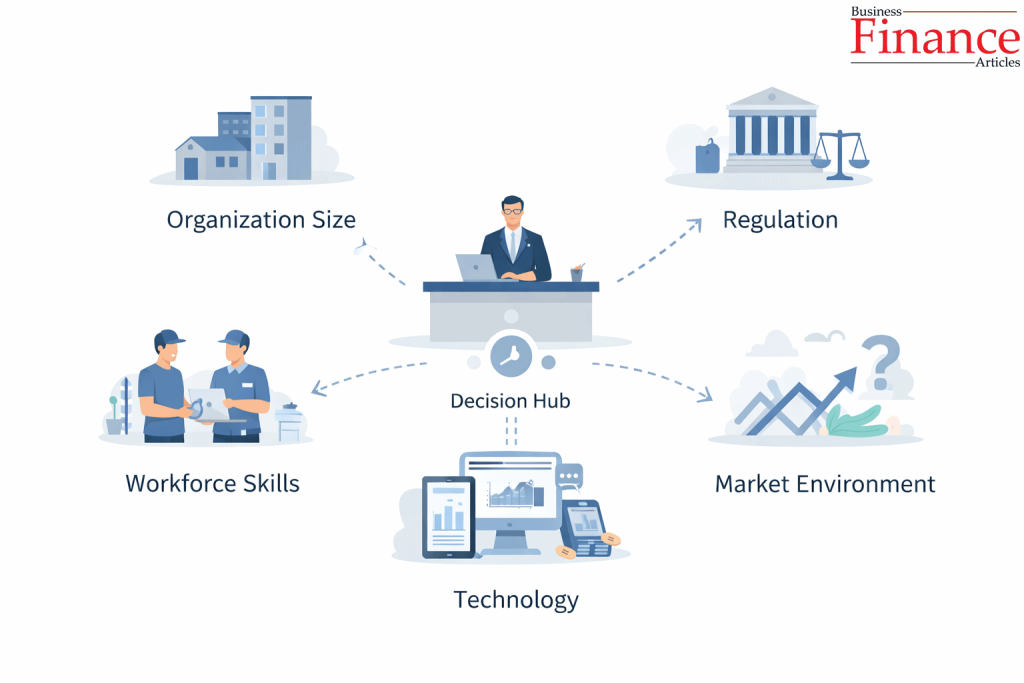
Factors affecting centralization are the organizational, environmental, and managerial conditions that determine how much decision-making authority should remain at the top versus being delegated downward.
There is no universal level of centralization. The right balance depends on context, not preference. These factors influence which types of centralization an organization adopts in practice.
1. Organizational Size
Why Size Matters
The size of an organization strongly influences the degree of centralization it can sustain.
- Small organizations often benefit from centralization because:
- Fewer employees mean easier coordination
- Leaders have direct visibility into operations
- Decision-making is faster with fewer layers
- Large organizations face limitations because:
- Centralized control becomes slow and overloaded
- Managers cannot oversee every unit effectively
- Local responsiveness becomes critical
Practical Insight: As organizations grow, pure centralization becomes impractical. Most large firms shift toward partial decentralization while keeping strategy centralized.
2. Industry Regulation and Compliance
Why Regulation Encourages Centralization
Industries with strict regulatory requirements often rely on centralized control to ensure compliance, accuracy, and risk management.
Common examples include:
- Banking and finance
- Healthcare
- Aviation
- Government and public administration
In these sectors, deviations from policy can result in:
- Legal penalties
- Safety risks
- Loss of public trust
Practical Insight: The more regulated the industry, the stronger the case for centralized decision-making, especially for compliance, reporting, and governance. When applied correctly, centralization improves control and consistency—key advantages of centralization in large or regulated organizations.
3. Technology and Information Systems
Technology as an Enabler (or Constraint)
Technology plays a dual role in centralization:
- Centralized systems (ERP, centralized dashboards, unified databases) support:
- Top-level monitoring
- Standardized reporting
- Coordinated planning
- Collaborative and digital tools enable:
- Faster communication
- Distributed decision-making
- Real-time local insights
Practical Insight: When technology enables real-time visibility, organizations can centralize strategy while decentralizing execution without losing control.

4. Workforce Skill Level
Skill Determines Autonomy
The capability of employees directly affects how much authority can be delegated.
- Low-skill or standardized roles:
- Work best under centralized supervision
- Follow clear rules and procedures
- Require limited discretion
- Highly skilled or knowledge-based roles:
- Perform better with autonomy
- Require judgment and creativity
- Resist excessive control
Practical Insight: Organizations with skilled professionals often centralize goals and standards, but decentralize methods and decisions.
5. Market Volatility and Environmental Uncertainty
Stability vs Change
The external environment significantly shapes centralization decisions.
- Stable markets favor centralization because:
- Predictability reduces risk
- Long-term planning is reliable
- Uniform decisions work well
- Volatile markets require decentralization because:
- Conditions change rapidly
- Local teams need authority to respond
- Delays reduce competitiveness
Practical Insight: The faster the market changes, the less effective rigid centralization becomes.
6. Leadership Style and Management Philosophy
Leadership Shapes Structure
Leaders play a decisive role in determining centralization levels.
- Authoritative or control-oriented leaders:
- Prefer centralized authority
- Value uniformity and discipline
- Retain decision-making power
- Participative or transformational leaders:
- Encourage delegation
- Trust employee judgment
- Support decentralized structures
Practical Insight: Organizational structure often reflects leadership mindset more than operational need, which can either strengthen or weaken performance. Ignoring these conditions often leads to rigidity and delays, common disadvantages of centralization.
How These Factors Work Together
These factors do not operate independently. They interact.
For example:
- A large organization in a regulated industry may centralize compliance but decentralize operations.
- A technology-driven firm with skilled employees may centralize strategy while decentralizing innovation.
- A volatile market combined with rigid leadership often leads to structural failure.
Organizations that ignore these interacting factors frequently encounter systemic risks caused by poor centralization decisions.
Centralization Is a Degree, Not a Choice
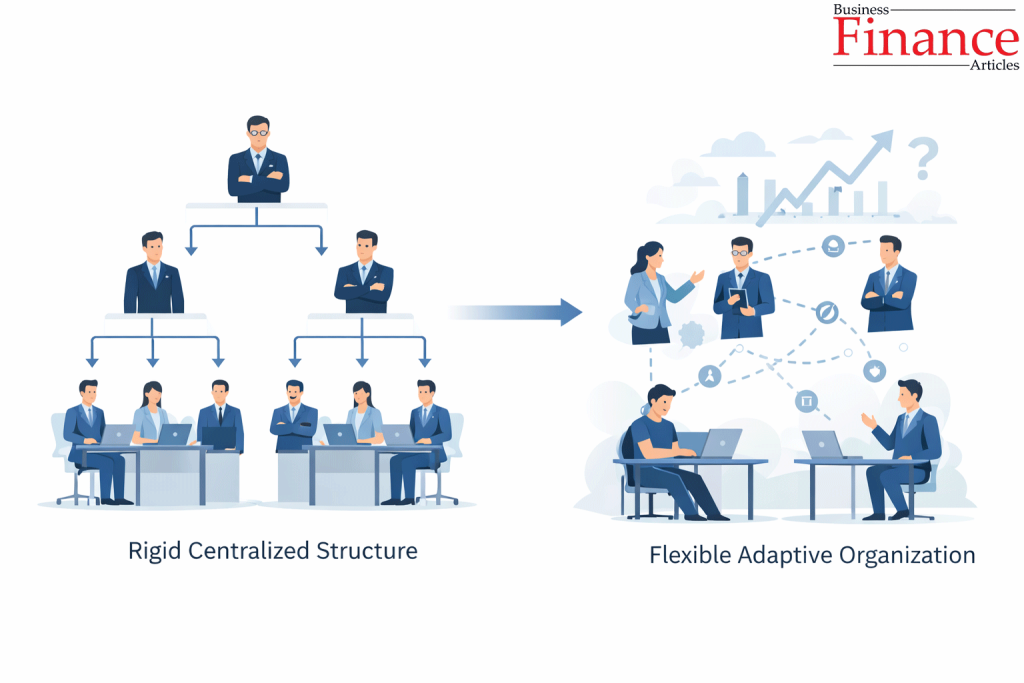
One of the most common mistakes is treating centralization as an either-or decision. This reflects the debate of centralization vs decentralization, where organizations balance control with flexibility.
In reality:
- No organization is fully centralized
- No organization is fully decentralized
- Effective structures adjust authority dynamically
This aligns with classical management thinking, including Henri Fayol’s view that centralization exists on a continuum.
Final Takeaway
Factors affecting centralization help organizations decide wisely, not blindly. Size, regulation, technology, skills, market conditions, and leadership style all shape how authority should flow.
Centralization succeeds when it fits the context.
It fails when it ignores these factors.
Organizations that evaluate these conditions carefully are far more likely to design structures that scale, adapt, and perform.
FAQs
What factors influence centralization?
Organizational size, regulation, technology, skills, leadership style, and market stability.
Does technology support centralization?
Yes, centralized systems enhance monitoring and control.
Is centralization suitable for volatile markets?
Usually no. Volatile markets require flexibility and faster decisions.

The BusinessFinanceArticles Editorial Team produces research-driven content on business, finance, management, economics, and risk management. Articles are developed using authoritative sources, academic frameworks, and industry best practices to ensure accuracy, clarity, and relevance. Learn more about the BusinessFinanceArticles Editorial Team
Leave a Reply