Quick Answer: The main factors of globalization include technological advancement, improved transportation and containerization, economic integration, trade liberalization and tax policies, government policies, infrastructure development, and changes in production and consumption patterns. These factors collectively enable the expansion of business, trade, and communication across national borders.
Globalization has transformed how countries, businesses, and societies interact with one another. In today’s interconnected world, goods, services, capital, technology, and information move across borders more easily than ever before. This global integration has not occurred by chance; it is driven by several economic, technological, political, and infrastructural factors.
This article explains the major factors of globalization, how they contribute to global integration, and why they are important in the modern world economy.
What is Globalization?
Globalization refers to the process by which countries, economies, businesses, and societies become increasingly interconnected and interdependent through international trade, investment, technology, communication, and cultural exchange.
It goes beyond business expansion and includes the global flow of goods, services, capital, labor, information, and ideas. Globalization allows organizations to operate on an international scale while enabling consumers to access products and services from different parts of the world.
Why Do We Study the Factors of Globalization?
Understanding the factors of globalization helps explain:
- How international trade expands
- Why businesses operate across borders
- How economies become interconnected
- Why global competition increases
These factors provide insight into how globalization develops and why it continues to shape the modern economic system.
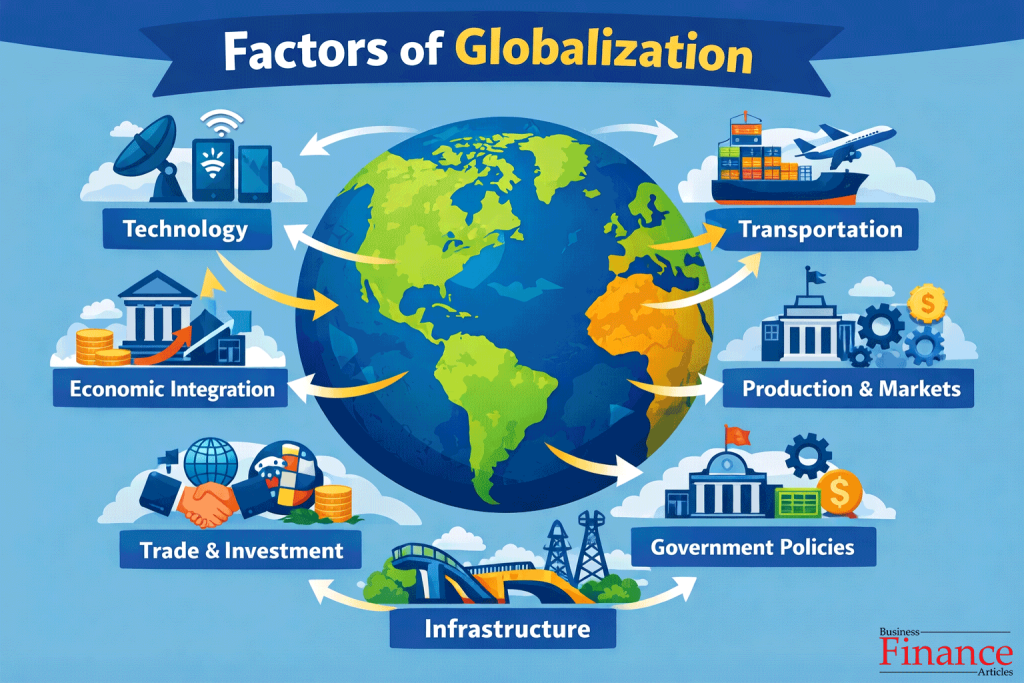
Major Factors of Globalization and Their Role
| Factor of Globalization | How It Contributes to Globalization |
| Technological Advancement | Enables fast communication, digital transactions, and global coordination |
| Transportation & Containerization | Reduces cost, time, and risk of international trade |
| Economic Factors | Encourages specialization, trade, and cross-border investment |
| Trade Liberalization & Tax Policies | Lowers trade barriers and attracts foreign businesses |
| Government Policies | Supports or restricts global trade and investment |
| Infrastructure Development | Improves connectivity, logistics, and market access |
| Production & Market Strategies | Allows firms to operate and scale globally |
“These factors work together rather than independently to drive globalization.”
Major Factors of Globalization
Technological Advancement
Technological progress is one of the most important factors of globalization. Advances in information and communication technology have made it easier for businesses and individuals to connect across borders.
The development of the internet, email, video conferencing, and digital platforms allows companies to communicate with customers, suppliers, and partners worldwide in real time. Technology has reduced transaction costs, improved coordination, and enabled global business operations to function efficiently.
As a result, technology has removed many geographical barriers and accelerated the pace of globalization.
Transportation and Containerization
Improvements in transportation systems have significantly contributed to globalization. Modern shipping methods, especially containerization, have reduced the cost, time, and risk involved in transporting goods internationally.
Standardized containers allow goods to be transported safely and efficiently across ships, trucks, and railways without repeated handling. This has made international trade more reliable and affordable, even for large volumes of goods.
Efficient transportation networks enable businesses to access global markets and integrate international supply chains, making containerization a key driver of globalization.
Economic Factors
Economic conditions play a major role in shaping globalization. Differences in production costs, resource availability, and consumer demand across countries encourage international trade and specialization.
Purchasing power, income levels, and consumer preferences influence the flow of goods between regions. Developed economies often focus on quality and innovation, while developing economies may prioritize affordability and mass production.
In addition, financial globalization has made international fund transfers faster and more efficient, allowing capital to move across borders and support global trade and investment.
Trade Liberalization and Tax Policies
Trade liberalization is an important factor of globalization. Reduction of trade barriers such as tariffs, quotas, and restrictions encourages cross-border trade and investment.
Tax policies also influence globalization by attracting or discouraging foreign businesses. Competitive tax rates, investment incentives, and trade agreements motivate companies to operate internationally and establish global operations.
Supportive trade and tax frameworks help integrate national economies into the global market.
Government Policies
Government policies play a crucial role in promoting or restricting globalization. Political stability, economic reforms, and supportive regulations encourage international trade and foreign investment.
Governments that invest in trade agreements, ease business regulations, and support export-oriented industries create an environment favorable to globalization. Conversely, restrictive policies can slow global integration.
Thus, government decisions significantly shape the direction and extent of globalization.
Infrastructure Development
Infrastructure is a foundational factor of globalization. Efficient ports, roads, railways, airports, power supply, and digital infrastructure enable smooth movement of goods, services, and information.
Countries with strong infrastructure systems are better positioned to participate in global trade and attract international businesses. Infrastructure development reduces operational costs and improves connectivity, supporting globalization at both national and international levels.
Production and Market Expansion Strategies
Globalization is also driven by changes in production and business strategies. Companies seek global markets to achieve economies of scale, diversify risks, and increase profitability.
Advancements in production techniques allow firms to locate different stages of production in different countries based on cost and efficiency. This global distribution of production activities strengthens international supply chains and accelerates globalization.
Importance of These Factors in the Modern World
In the modern economy, these factors work together to:
- Increase global trade and investment
- Enhance competition and innovation
- Expand consumer choice
- Strengthen international economic integration
Globalization today is not driven by a single factor but by the combined effect of technology, economics, policy, and infrastructure.
Challenges and Limitations of Globalization (Brief Note)
While globalization offers many benefits, it also presents challenges such as unequal economic development, job displacement, and increased competition for local industries. These challenges highlight the need for balanced policies and sustainable globalization strategies.
Conclusion
The factors of globalization explain how and why the world has become increasingly interconnected. Technological advancement, transportation and containerization, economic integration, trade policies, government support, infrastructure development, and modern production strategies collectively drive globalization.
Understanding these factors is essential for students, policymakers, and businesses seeking to navigate and succeed in the global economy. As global integration continues to evolve, these factors will remain central to shaping international trade and economic development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main factors of globalization?
The main factors of globalization include technological advancement, improved transportation and containerization, economic integration, trade liberalization, government policies, infrastructure development, and changes in production and consumption patterns.
How does technology contribute to globalization?
Technology contributes to globalization by enabling faster communication, reducing transaction costs, and allowing businesses to operate and coordinate activities across national borders through digital platforms and information systems.
Why is transportation important for globalization?
Transportation is important for globalization because efficient logistics and containerization reduce the cost, time, and risk of moving goods internationally, making global trade more accessible and reliable.
What role do government policies play in globalization?
Government policies influence globalization by shaping trade regulations, foreign investment rules, taxation systems, and economic reforms. Supportive policies encourage global integration, while restrictive policies can limit it.
How do economic factors affect globalization?
Economic factors such as differences in production costs, purchasing power, resource availability, and consumer demand encourage countries to specialize and trade internationally, thereby promoting globalization.
Is globalization driven by a single factor?
No, globalization is not driven by a single factor. It results from the combined impact of technology, transportation, economic forces, government policies, infrastructure, and global business strategies working together.

The BusinessFinanceArticles Editorial Team produces research-driven content on business, finance, management, economics, and risk management. Articles are developed using authoritative sources, academic frameworks, and industry best practices to ensure accuracy, clarity, and relevance. Learn more about the BusinessFinanceArticles Editorial Team
Leave a Reply